If done well, SEO (search engine optimization) can send thousands of targeted visitors to your website every month.
This turns your site from an afterthought into an asset that generates leads and sales.
Backlinko started as a simple personal blog in 2012, publishing one or two posts per month. In the first two years, our traffic grew from a few hundred monthly visitors to several thousand.
Now it generates over 680K monthly sessions, with 74% coming from organic searches.

It has taken over a decade to reach this point, but our approach to SEO has remained consistent. It’s always been about helpful content, thoughtful user experience, strong branding, and earning quality backlinks.
This article covers how to do SEO for your website in 10 digestible steps. And recommended tools along the way (some free and some paid).
We interviewed Andrew Peluso, owner of Bananas Marketing Agency, for his expert advice on getting started with SEO. You’ll see his tips throughout this guide to set your small business up for success.
Okay, ready?
Let’s start with step one.
If you haven’t already set up your site, it’s time to choose a platform.
Choose one that matches your technical skill level and business needs. For example, many website builders offer drag-and-drop editors. Making it easier for you to design and customize sites.
Here are a few options:

Further reading: 10 Steps to Create a Website (from Scratch)
Consider using WordPress as it gives you more technical flexibility to improve your rankings.

“A simple, well-done WordPress website is going to give you the best chance at ranking. I recommend finding a YouTube tutorial to help you build your WordPress site.”
While website builders are popular, they may not be the best choice because they limit your control over the backend of your website.
As your business grows and your SEO needs become more complex, these limitations might hinder your progress.

“The problem with something like Wix, in particular, is that if you take SEO seriously, then, eventually you get to the point where you’re going to have to graduate out of the platform anyways. Wix as a builder is going to limit the control you have over the backend, HTML, and JavaScript functions. Eventually, you’re going to need that control, and WordPress is the best platform for getting that control.”
WordPress includes many plugins and themes to enhance your SEO efforts. And make your site more user-friendly. Including Elementor, which helps you easily design your website with templates.
Regardless of the platform you choose, follow these key steps when building a new website:
Your domain name is your website’s address on the internet.
So, choose a domain name that’s:
For example, Backlinko.com is unique, memorable, and concise. It’s also relevant to our audience—backlinks are a major topic in the SEO industry.

Your website’s theme determines its overall look and feel. Choose a preset theme that aligns with your brand identity and is mobile-responsive.
Then, customize it to make it your own.
To create a consistent and memorable brand, add your:

Further reading: SEO-Friendly Web Design
Security measures are essential for user trust and SEO, as Google prioritizes secure websites in search results.
Secure your website with an SSL certificate (HTTPS) to protect your visitors’ information using data encryption.
Here’s how a security certificate appears on a website:

Many hosting providers offer free SSL certificates with their plans, making it easy to add this layer of security to your website.
Check with your hosting provider to see if this is included. If not, look for a plugin. For example, on WordPress, you can use Really Simple SSL.

Further reading: Blog Design: The Complete Guide
More than half of all web traffic comes from mobile devices. So, ensure your website is mobile-responsive. Meaning it adapts to different screen sizes.
Most modern themes and website templates offer responsive designs. But you can easily test how mobile-friendly your site is by accessing it on your smartphone or tablet.
Here’s what to look for during your mobile test:

Further reading: Mobile SEO: The Definitive Guide
Learning how to do SEO for a website includes researching your customers, competitors, and keywords. So, you can optimize your site for your target audience and search engines.
Understanding what your audience is searching for online is the foundation of a successful SEO strategy.
First, put yourself in your customers’ shoes and brainstorm questions they might have about your product, service, or industry.
Think about their:
Make a list of questions your customers ask in person, over the phone, or through marketing channels like email and social media.
Additional ways to do audience research include:


Research your competitor’s websites to find keywords they’re using to reach people. Since these keywords drive traffic to your competitors, they could also benefit your SEO strategy.
Note: We’ll be using Semrush to show you how to do competitive research. You can analyze up to 10 domains per day on a free account. Or you can use this link to access a 14-day trial on a Semrush Pro subscription.
Say you’re doing SEO research for your hairdressing salon in Miami. One of your main competitors is Blunt Blonde Salon.
Open Semrush’s Organic Research tool, enter “bluntblondesalon.com”, and select “US” as your target country. Hit “Search.”

We can see Blunt Blonde Design targets 265 keywords and is estimated to receive 315 visitors from organic traffic in the next month.

Scroll past the overview to the “Top Keywords” section. Where you’ll find a list of the most popular search terms.
Click “View all keywords” to open the full list of all the keywords used across this website.

Review the keywords to see which ones you’d like to target in content.

Click the checkbox next to the ones you’re interested in to save them to a list.
Click “+Add to keyword list” and give your list a name (optional).

To access your list of saved keywords, click your list. Or navigate to Keyword Strategy Builder from the left-hand menu. And select your list.

If you’d like to keep your keywords in a spreadsheet, click “Export” and select your preferred format.

By now, you should have a list of potential keyword ideas from your customer and competitor research.
At this point, use a keyword research tool like Semrush’s Keyword Magic tool. This tool will help you discover additional terms. And refine your list based on data like:
Enter one of your keywords in the Keyword Magic Tool, select your target region, and click “Search.”
Let’s say you want to target customers looking for curly haircuts.
Type the keyword, “curly haircuts” into the tool to research its popularity.

The Keyword Magic tool will populate relevant search terms. Like “mens curly haircuts” and “short curly haircuts.”
“Mens curly haircuts” could be a good term to target because it gets over 9,900 daily searches and has an “easy” keyword difficulty rating.

Select the “Questions” filter to narrow your search to questions your audience searches for. Like “what is the best haircut for curly hair.”

Add any relevant keywords and questions to the keyword list you created when you researched the keywords.
Use the questions and search terms you researched to guide your website’s structure.
Andrew suggests mapping out what you want your website to look like. And ensuring it’s designed to answer your target audience’s questions.

“I would honestly just start with what your site architecture is going to look like. What pages do you need on your website to answer all of the questions that someone you’re trying to sell your product or service to is going to have?”
Site architecture is a navigational map of your website’s structure. It outlines the hierarchy of pages and how they connect. Like this:

A sitemap planning tool like Lucid can help you organize an SEO-friendly site architecture that appeals to your audience.
When creating your site structure, consider the following:
Another effective way to approach website structure is to look at your competitors. What pages do they have on their sites? What topics do they cover? Use their sites as inspiration for your structure.
Once you’ve identified your audience’s questions and structured your website to address them, the next step is to create high-quality, search engine-optimized content.
This kind of content aims to do two things:
Here’s how to create SEO content:
Every question or search query you collected earlier has an underlying intent.
Matching this intent helps you create content that satisfies users. And ranks highly.
There are four types of search intent:
When writing copy for your website, integrate relevant keywords on each page.
This includes:
This helps search engines understand what your content is about. And improves your chances of ranking for relevant searches.
In addition to your primary target keywords, consider including relevant secondary keywords. These are related terms or phrases that can further enhance your content’s relevance and visibility in search results.
Use a combination of primary and secondary keywords to attract a broader range of organic traffic.
Beyond keyword optimization, it’s equally important to demonstrate Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) in your content.
But what does it mean?
Google created its E-E-A-T framework to evaluate the quality of webpages. This means the search engine prioritizes trustworthy content created by experts.
Here’s how to comply with Google’s E-E-A-T guidelines:
For example, if you’re creating an article on how to fill out tax returns, you could ask an accountant to review it for accuracy.
If you’re creating a blog post on the best exercises to relieve back pain, you could ask a qualified physical therapist to demonstrate them in a video. Or provide expert quotes.
Prioritize E-E-A-T and create valuable content that resonates with your target audience. And you’ll have a better chance of improving your search rankings. Plus, you’ll build trust and credibility with your readers.
Headings (H1 through H6.) help organize your content and make it easier to read.
They also signal to search engines about the hierarchy and relevance of your content.
Here’s how to structure your content with headings:

On-page SEO is optimizing individual webpages to enhance their visibility in search engines and attract more organic traffic.
Since you’re just learning how to do SEO for a website, we’ll focus on three essential on-page SEO techniques that can influence your website’s visibility.
A title tag is a clickable headline in search results.
Each page on your website needs a unique title tag that tells users what to expect from the page.
Like this:

Keep title tags concise (50 to 60 characters) and descriptive. Incorporate your target keyword naturally.
A meta description is a brief summary of a webpage that appears below the title.
Like so:

Summarize the page’s content in 155 characters or fewer. Include relevant keywords. And make your meta description compelling so searchers want to click on it to read more.
Like a title tag, a meta description is also unique to each individual page of a website.
Internal links connect pages within your website. They show search engines like Google that pages on your website are relevant to each other. And helps readers get more in-depth information about the specific topic.
For example, our article about writing SEO content mentions keyword research. Because we already have an in-depth article about it, we included an internal link to lead our readers to that resource.
Like this:

Follow these internal linking best practices:
Anchor text is the clickable text in a hyperlink. It serves as a preview of the content users can expect to find when they click on the link.
In the context of SEO, anchor text provides information to search engines about the linked page’s topic.
When writing anchor text, include a keyword or its variation. And avoid linking to generic phrases like “click here.”
In our example, the target keyword for the article we linked to was “keyword research.”

So, we hyperlinked this keyword because it aptly describes the linked-to page’s content.
Ensure the pages you link to are contextually relevant to the current page.
For example, if you have a blog post about the benefits of yoga for stress relief, you could include internal links to other pages on your site about different yoga poses and meditation techniques.
This helps users discover related content. And signals to search engines that your pages are connected.
Image SEO is the act of optimizing an image so that it has a better chance of appearing higher in search results and Google Images.
For example, if you’re creating a webpage on “heating repair services,” you should also include that keyword in your image name for that page:

Here’s how to do image SEO:

You created valuable, search engine-optimized content.
That’s great.
But when your business website is new, you also need to establish credibility and authority through backlinks.
A backlink is a link from one website to another. It’s a signal for search algorithms that your website is trustworthy and has valuable information.
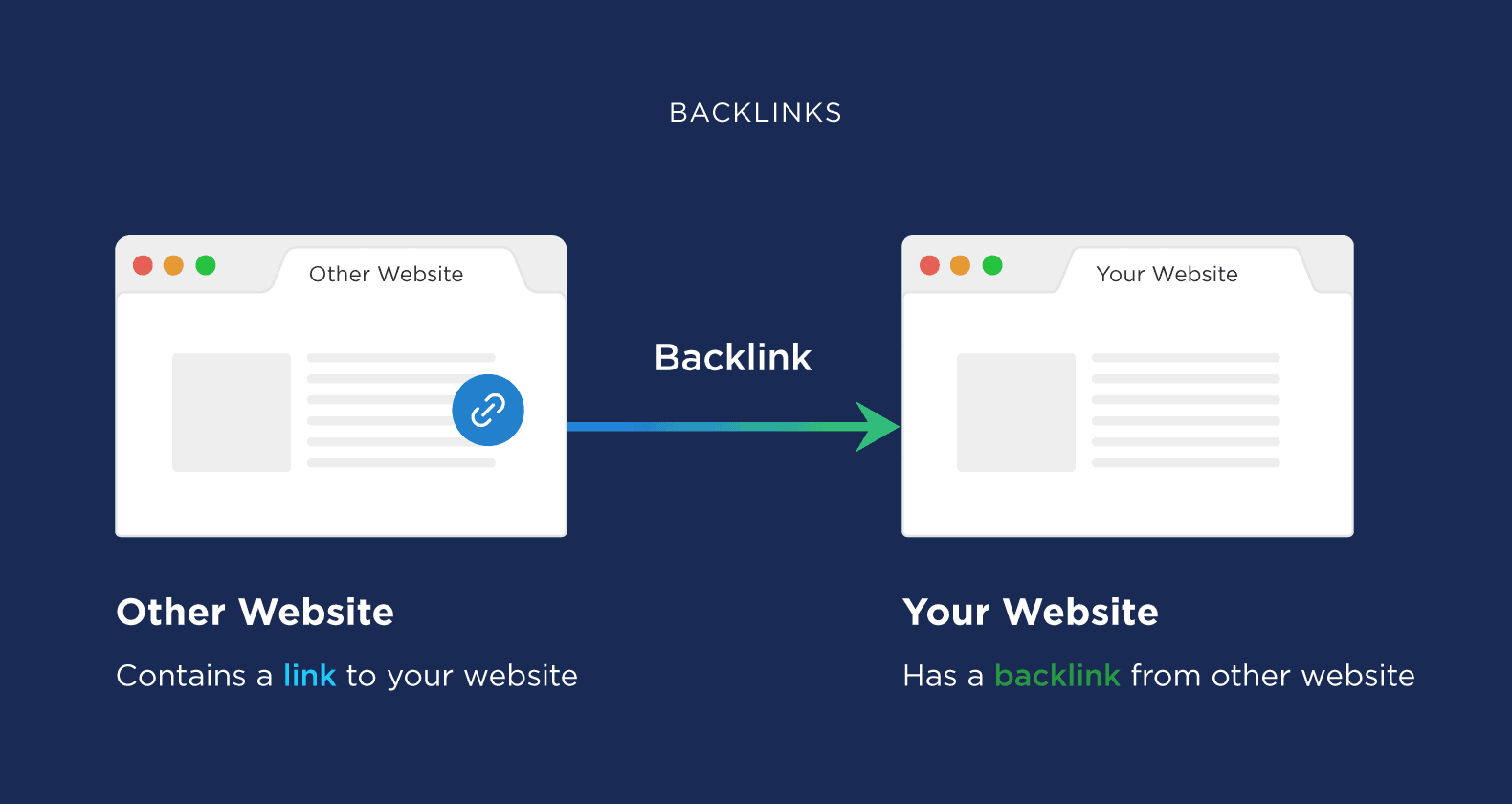
Having backlinks helps show Google you’re a legitimate business people talk about.
While there are multiple ways to acquire backlinks, Andrew recommends getting involved in your local community.
For example, if you get a booth at a local farmer’s market, the event site might include your logo and a link to your site, helping you build authority.

“I recommend involving yourself in the community because offline activities can result in backlinks. Not only are these backlinks going to show Google that you’re involved locally, but they’re also going to get more potential customers to engage with you because they see you’re involved offline as well.”
Here are a few ways to establish credibility and get high-quality backlinks:
Creating content and optimizing its on-page elements is just the start. Now, it’s time to promote your content across various platforms. To attract more visitors to your website.
Reaching a wider audience will help build your brand, establish authority, and increase your online visibility.
This increased traffic signals to search engines that your content is valuable and relevant. Which can positively impact your rankings.

Further reading: 22 Content Marketing Examples to Inspire You
A Google Business Profile (GBP) is a digital storefront where you can provide essential information about your business. Like your address and contact information.

GBP is a free tool by Google that allows you to manage your local business’s online presence across Google Search and Maps.
To get started, search for your business on Google. If Google has already created a profile for your business, claim it by verifying your ownership. If not, you can easily create a new profile by providing the required information.
Here’s what to keep in mind when setting up a Google Business Profile:
Your primary category is the most important for SEO, as it significantly influences what keywords your business appears for.
For example, a law firm specializing in civil law should narrow down its business category to “Civil law attorney” to increase its visibility for relevant searches.

If your business is seasonal, consider changing your main category to reflect peak demand.
For example, an HVAC repair service might prioritize “Air conditioning repair service” in the summer. And switch to “Heating contractor” in the winter.
Add high-quality photos that showcase your business, products, or services. Feature season-specific offerings if applicable.
Like photos of your team installing air conditioners in the summer or servicing heaters in the winter.
Double-check that your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) are consistent and accurate across all online platforms. This includes your website, social media profiles, and online directories like Yelp.
Positive reviews build trust and influence local search rankings. Encourage customers to leave reviews and respond promptly to both positive and negative feedback.

Further reading: Local SEO: The Definitive Guide
Set up analytics tools like Google Search Console (GSC) and Google Analytics (GA) to track your website’s performance and understand how visitors interact with your content.
Why both?
Let’s see how to set up each tool:
Open Google Search Console, enter your domain, and click “Continue.”

Next, you’ll see the instructions to verify your domain ownership:


Further reading: Google Search Console: The Definitive Guide
Open Google Analytics, name your account, and select account data sharing settings.
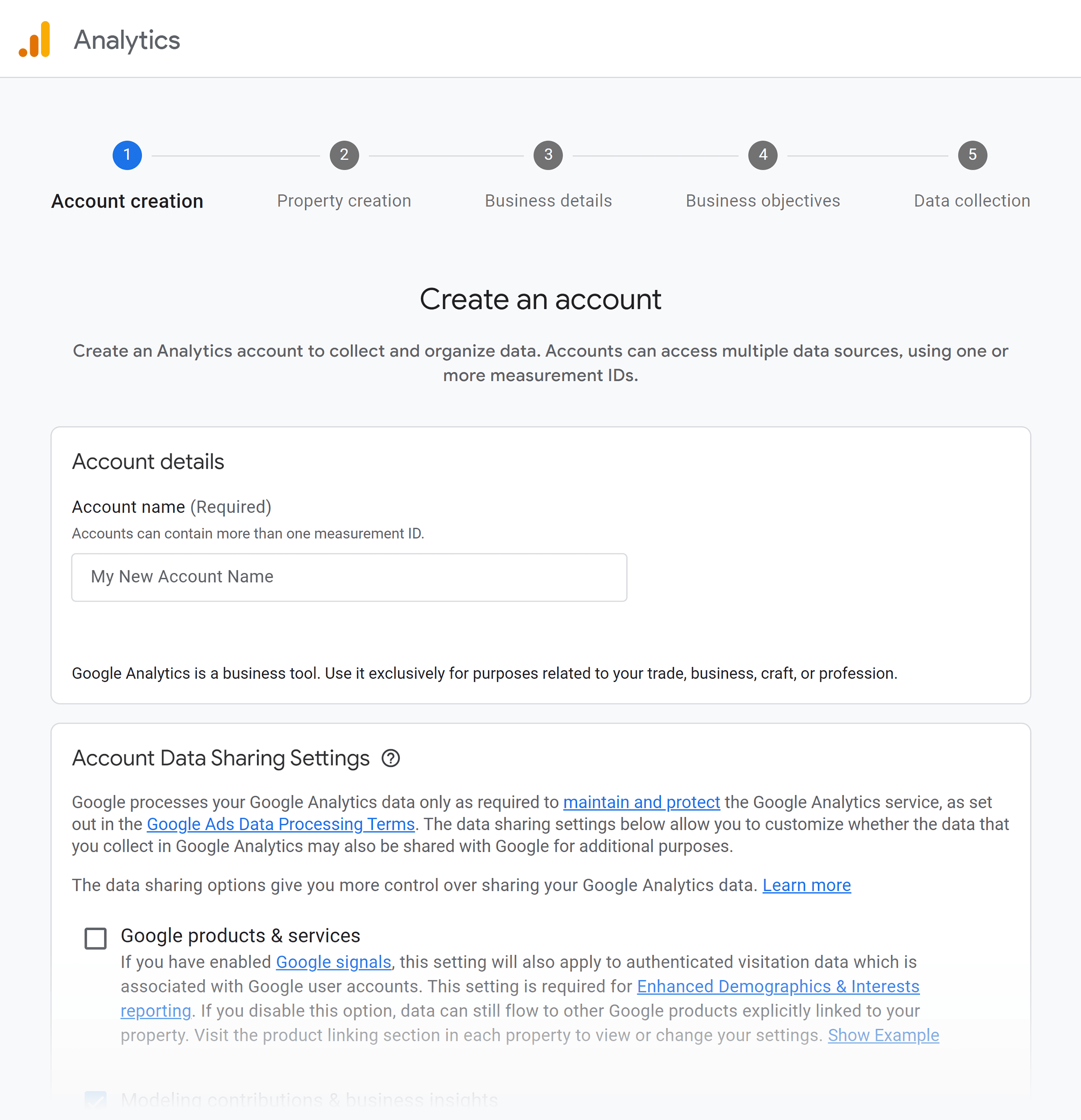
Then, scroll to “Next.”
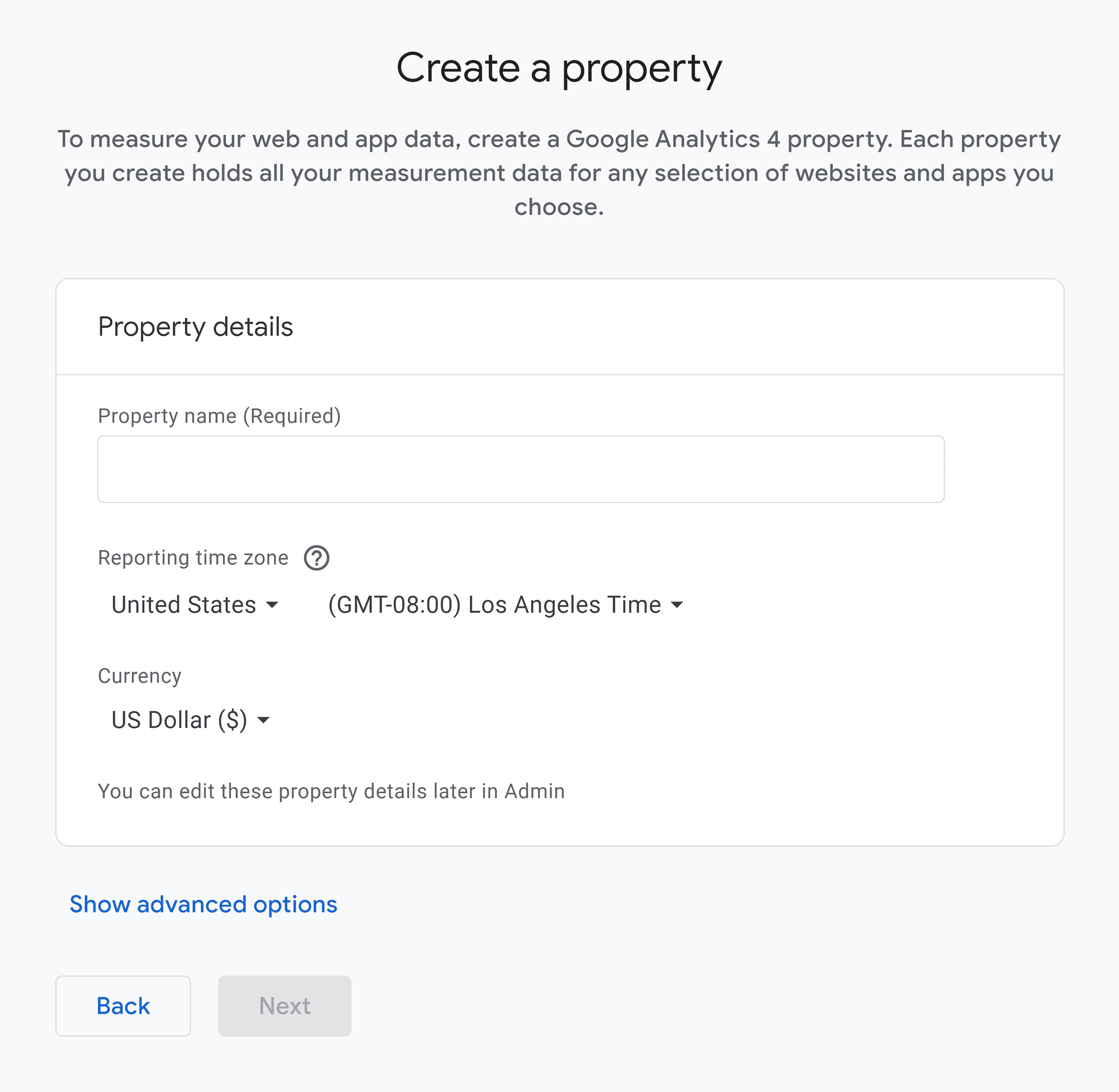
The next step is to create a property for your account. A property represents a website that you want to track and analyze.
Give your property a name and select your time zone and currency. Click “Next.”
Now, select your business details like industry and size.
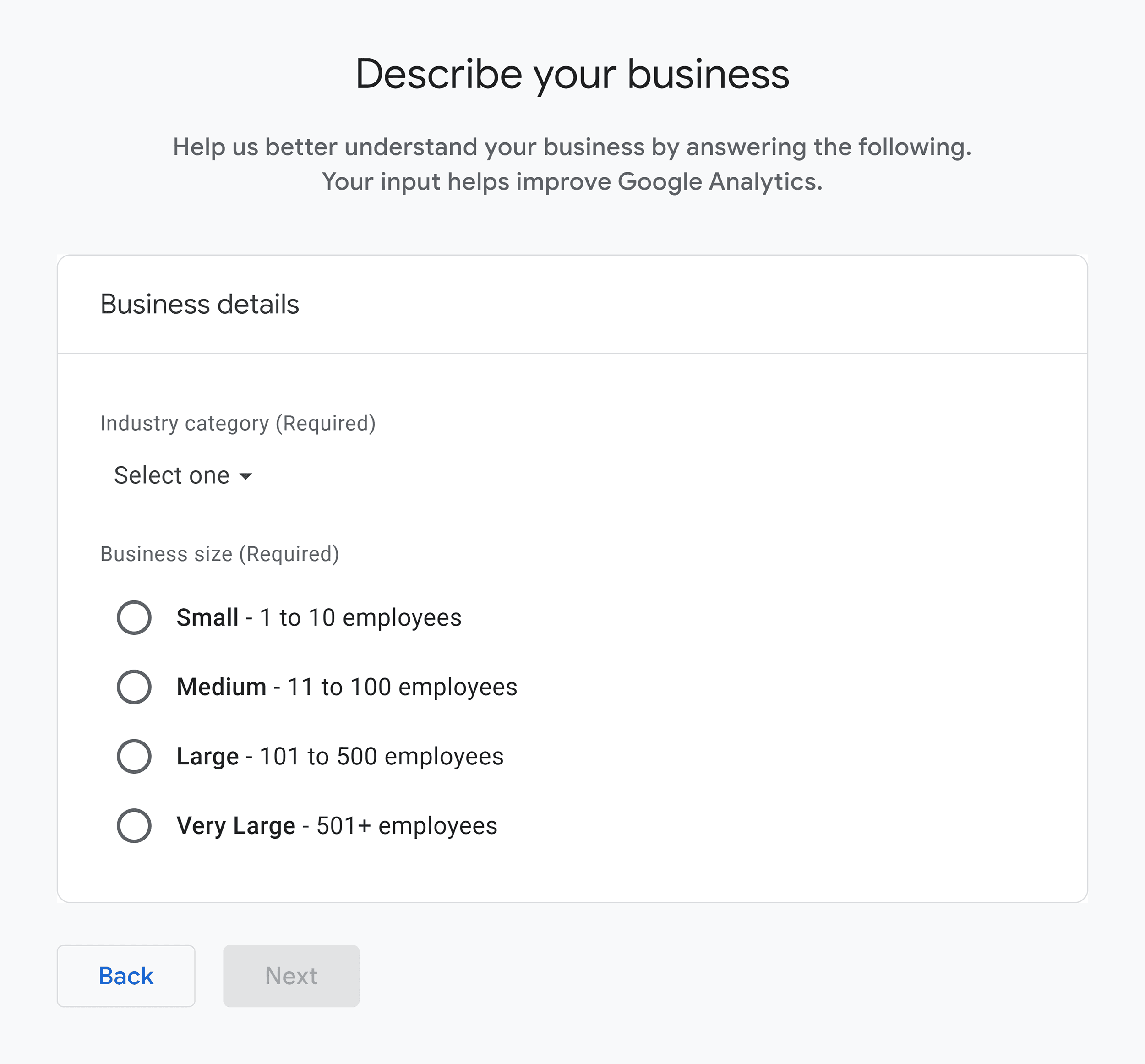
And your business objectives. Like generating leads, selling products or services, and raising brand awareness.
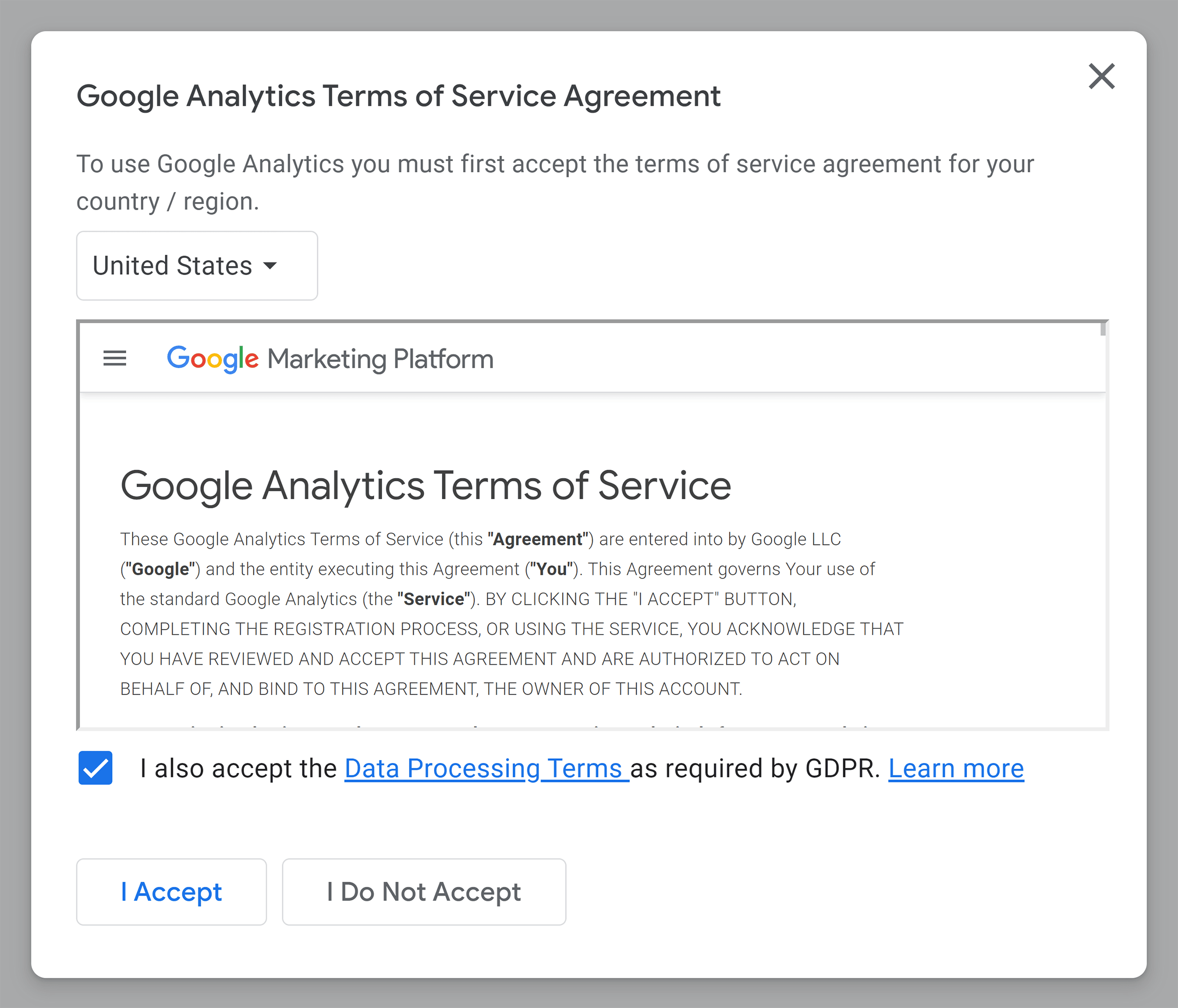
Accept Google Analytics Terms of Service Agreement.
Select the platform you’d like to start collecting data from (like a website, Android app, or iOS app).
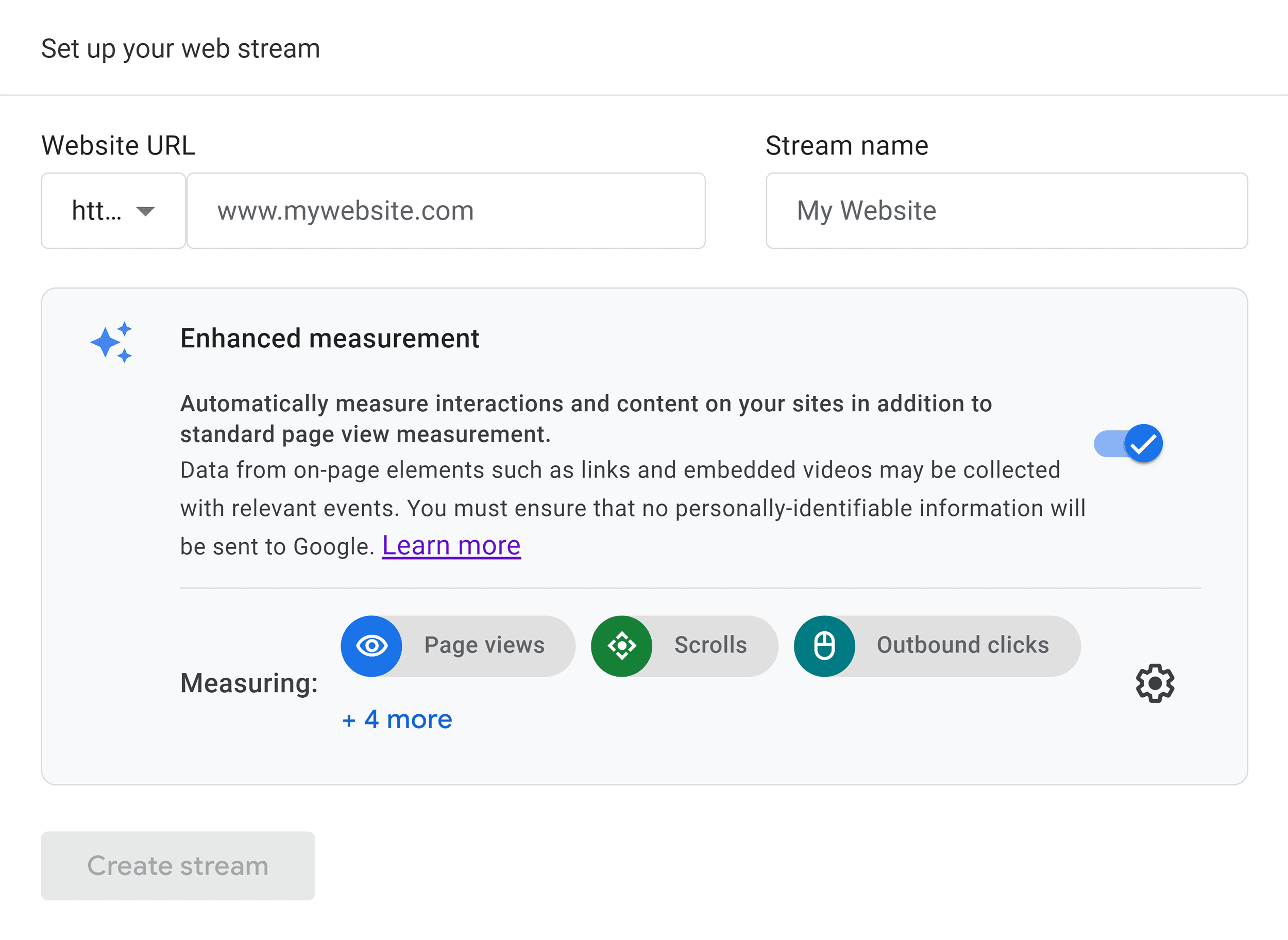
In your case, select “Web.”
Enter your website URL and type “My Website” in the “Stream name” field. Click “Create stream.”
Select your website builder and follow the instructions for that specific platform.


Further reading: Google Analytics (GA): Ultimate Guide and Tutorial
Sign up for a free 14-day Semrush trial to monitor your GSC and GA data in one dashboard.
Combining data from various sources gives you a holistic view of your website’s performance. And lets you identify areas for improvement in one place.
Once you’ve set up Google Search Console and Google Analytics, integrate them into Semrush for a unified view.
Sign in to your Semrush account and navigate to “SEO Dashboard” from the left menu.

Enter your website name and click “Start now.”

Navigate to the “SEO Dashboard” again and select the settings icon at the top right corner of the screen. Select “Set up Google account” from the drop-down menu.
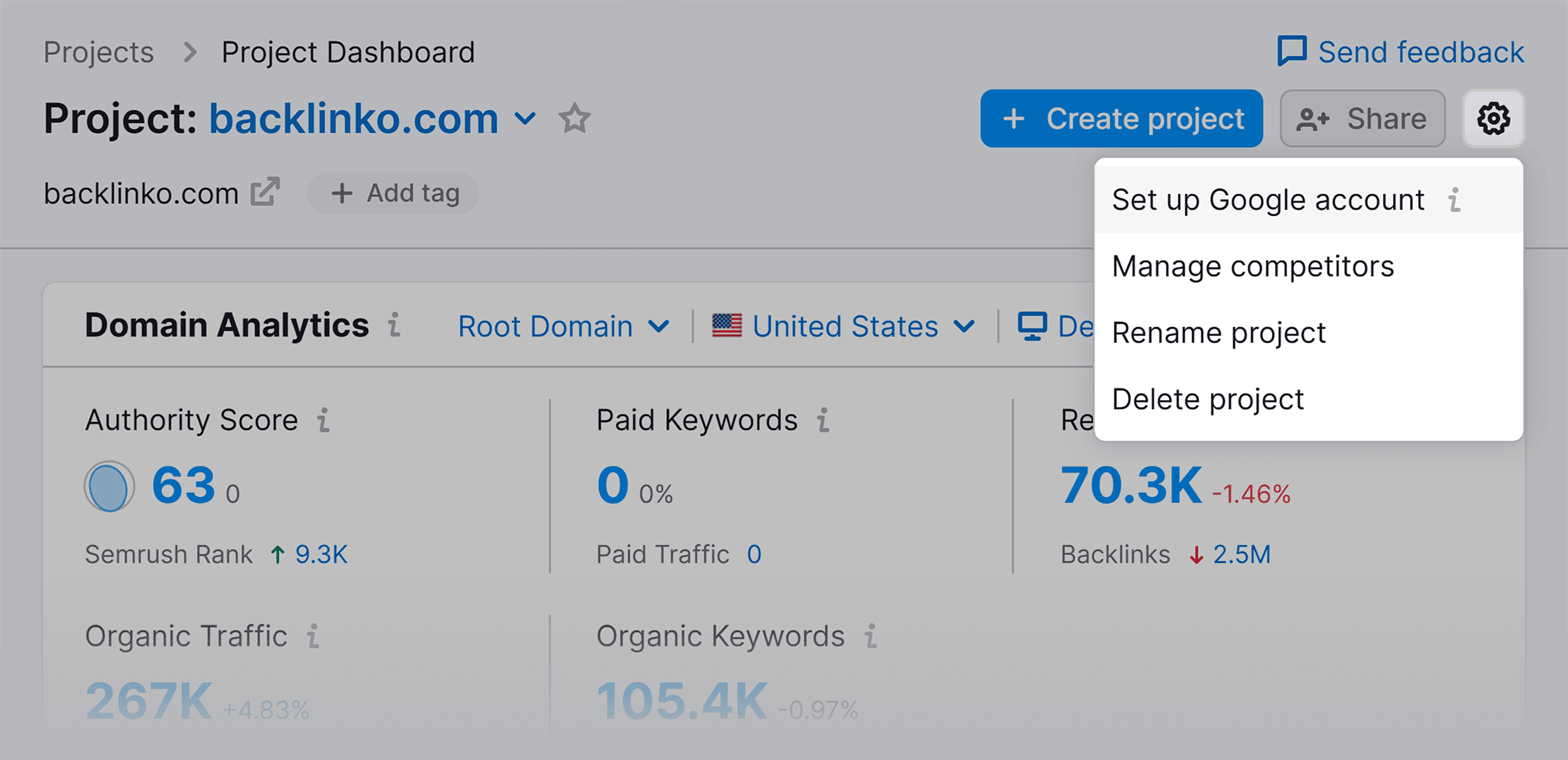
Select the email you used to set up your Google Search Console and Google Analytics.
Then, select your GA and GSC properties. And click “Save changes.”

Semrush will fetch data from GA and GSC for an aggregate view.
Scroll until you see “Traffic Analytics” and “Google Search Console Performance.” And review your site’s performance without having to log into multiple accounts.

Once you’ve learned how to do SEO for your website, your work isn’t done.
Regularly monitor your SEO performance to understand what’s working and what needs improvement. So, you can maintain or improve your rankings.
Impressions represent the number of times a user sees your website in search results. Even if they didn’t click it.
Having any number of impressions is a positive sign, as it indicates your site is indexed and discoverable.
Open Google Search Console, click on “Search results” under the “Performance” section, and select “Total Impressions.”

Not seeing impressions for keywords you want to rank for may mean your content isn’t indexed or optimized well enough.
Or that Google doesn’t consider your website relevant for those queries.
The solution is to revisit the content and update it to fix any issues to help it rank higher. And get more impressions.
Use relevant keywords naturally throughout your content. Include them in headings, meta descriptions, and image alt text.
A click is a user action that signifies a visitor found your link in the search results and chose to visit your website.
Clicks show that your rankings are high enough to attract organic traffic.
Scroll past the general performance results in Google Search Console and select the “Pages” tab to see which pages get the most clicks.
It should look something like this:

If you’re getting impressions but few or no clicks, this means your website shows up in search results, but users aren’t clicking on it.
This could be due to a couple of reasons:
The click-through rate reflects the percentage of impressions that resulted in a click.
Monitor click-through rates (CTR) for different queries to see which pages perform well. And which ones need improvement.
To see which keywords get the highest CTR, and which ones get the lowest, select the “Queries” tab. Like this:

SEO is an ongoing process that requires patience and dedication. With consistent effort, you can steadily improve your website’s visibility, attract more organic traffic, and achieve your business goals.
It’s important to have realistic expectations. As Andrew says, many people make the mistake of giving up on SEO too early, not realizing it’s a long-term investment.

“Remember, you’re five to 10 years and many thousands of dollars behind your competitors. Don’t get discouraged if you don’t see immediate results.”
Focus on building a strong foundation by creating valuable content and understanding your audience and their needs. Over time, your efforts can lead to sustainable growth and success.
Understanding the art of SEO copywriting can help you write content that resonates with your audience and search engines.
Learn everything you need to know in our free SEO copywriting guide. From optimizing your content to improving the user experience.